A newer version of the Gradio SDK is available:
5.11.0
Inference Servers
One can connect to Hugging Face text generation inference server, gradio servers running h2oGPT, or OpenAI servers.
Hugging Face Text Generation Inference Server-Client
Local Install
Not Recommended
This is just following the same local-install.
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | sh
source "$HOME/.cargo/env"
PROTOC_ZIP=protoc-21.12-linux-x86_64.zip
curl -OL https://github.com/protocolbuffers/protobuf/releases/download/v21.12/$PROTOC_ZIP
sudo unzip -o $PROTOC_ZIP -d /usr/local bin/protoc
sudo unzip -o $PROTOC_ZIP -d /usr/local 'include/*'
rm -f $PROTOC_ZIP
git clone https://github.com/huggingface/text-generation-inference.git
cd text-generation-inference
Needed to compile on Ubuntu:
sudo apt-get install libssl-dev gcc -y
Use BUILD_EXTENSIONS=False instead of have GPUs below A100.
conda create -n textgen -y
conda activate textgen
conda install python=3.10 -y
export CUDA_HOME=/usr/local/cuda-11.8
BUILD_EXTENSIONS=True make install # Install repository and HF/transformer fork with CUDA kernels
cd server && make install install-flash-attention
NCCL_SHM_DISABLE=1 CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 text-generation-launcher --model-id h2oai/h2ogpt-oig-oasst1-512-6_9b --port 8080 --sharded false --trust-remote-code --max-stop-sequences=6
Docker Install
Recommended
# https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/ubuntu/
sudo snap remove --purge docker
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install ca-certificates curl gnupg
sudo install -m 0755 -d /etc/apt/keyrings
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg
sudo chmod a+r /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg
echo "deb [arch="$(dpkg --print-architecture)" signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \
"$(. /etc/os-release && echo "$VERSION_CODENAME")" stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-plugin
sudo apt-get install -y nvidia-container-toolkit
sudo docker run hello-world
# https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/linux-postinstall/
sudo groupadd docker
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
newgrp docker
docker run hello-world
sudo nvidia-ctk runtime configure
sudo systemctl stop docker
sudo systemctl start docker
Reboot or run:
newgrp docker
in order to log in to this user.
Then run:
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0
docker run --gpus device=0 --shm-size 2g -e CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=$CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES -e TRANSFORMERS_CACHE="/.cache/" -p 6112:80 -v $HOME/.cache:/.cache/ -v $HOME/.cache/huggingface/hub/:/data ghcr.io/huggingface/text-generation-inference:0.8.2 --model-id h2oai/h2ogpt-gm-oasst1-en-2048-falcon-7b-v2 --max-input-length 2048 --max-total-tokens 4096 --sharded=false --disable-custom-kernels --trust-remote-code --max-stop-sequences=6
or
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
docker run --gpus all --shm-size 2g -e CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=$CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES -e TRANSFORMERS_CACHE="/.cache/" -p 6112:80 -v $HOME/.cache:/.cache/ -v $HOME/.cache/huggingface/hub/:/data ghcr.io/huggingface/text-generation-inference:0.8.2 --model-id h2oai/h2ogpt-oasst1-512-12b --max-input-length 2048 --max-total-tokens 4096 --sharded=true --num-shard=4 --disable-custom-kernels --trust-remote-code --max-stop-sequences=6
or for 20B NeoX on 4 GPUs
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
docker run --gpus all --shm-size 2g -e CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=$CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES -e TRANSFORMERS_CACHE="/.cache/" -p 6112:80 -v $HOME/.cache:/.cache/ -v $HOME/.cache/huggingface/hub/:/data ghcr.io/huggingface/text-generation-inference:0.8.2 --model-id h2oai/h2ogpt-oasst1-512-20b --max-input-length 2048 --max-total-tokens 4096 --sharded=true --num-shard=4 --disable-custom-kernels --trust-remote-code --max-stop-sequences=6
or for Falcon 40B on 2 GPUs
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=1,2
sudo docker run --gpus all --shm-size 1g -e CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=$CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES -e HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN=$HUGGING_FACE_HUB_TOKEN -e TRANSFORMERS_CACHE="/.cache/" -p 6112:80 -v $HOME/.cache:/.cache/ -v $HOME/.cache/huggingface/hub/:/data ghcr.io/huggingface/text-generation-inference:0.8.2 --model-id h2oai/h2ogpt-gm-oasst1-en-2048-falcon-40b-v2 --max-input-length 2048 --max-total-tokens 4096 --max-stop-sequences 6 --sharded true --num-shard 2
If one changes the port 6112 for each docker run command, any number of inference servers with any models can be added.
Testing
Python test:
from text_generation import Client
client = Client("http://127.0.0.1:6112")
print(client.generate("What is Deep Learning?", max_new_tokens=17).generated_text)
text = ""
for response in client.generate_stream("What is Deep Learning?", max_new_tokens=17):
if not response.token.special:
text += response.token.text
print(text)
Curl Test:
curl 127.0.0.1:6112/generate -X POST -d '{"inputs":"<|prompt|>What is Deep Learning?<|endoftext|><|answer|>","parameters":{"max_new_tokens": 512, "truncate": 1024, "do_sample": true, "temperature": 0.1, "repetition_penalty": 1.2}}' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' --user "user:bhx5xmu6UVX4"
Integration with h2oGPT
For example, server at IP 192.168.1.46 on docker for 4 GPU system running 12B model sharded across all 4 GPUs:
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3
docker run --gpus all --shm-size 2g -e CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=$CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES -e TRANSFORMERS_CACHE="/.cache/" -p 6112:80 -v $HOME/.cache:/.cache/ -v $HOME/.cache/huggingface/hub/:/data ghcr.io/huggingface/text-generation-inference:0.8.2 --model-id h2oai/h2ogpt-oasst1-512-12b --max-input-length 2048 --max-total-tokens 4096 --sharded=true --num-shard=4 --disable-custom-kernels --trust-remote-code --max-stop-sequences=6
Then generate in h2oGPT environment:
SAVE_DIR=./save/ python generate.py --inference_server="http://192.168.1.46:6112" --base_model=h2oai/h2ogpt-oasst1-512-12b
Gradio Inference Server-Client
You can use your own server for some model supported by the server's system specs, e.g.:
SAVE_DIR=./save/ python generate.py --base_model=h2oai/h2ogpt-oasst1-512-12b
In any case, for your own server or some other server using h2oGPT gradio server, the client should specify the gradio endpoint as inference server. E.g. if server is at http://192.168.0.10:7680, then
python generate.py --inference_server="http://192.168.0.10:7680" --base_model=h2oai/h2ogpt-oasst1-falcon-40b
One can also use gradio live link like https://6a8d4035f1c8858731.gradio.live or some ngrok or other mapping/redirect to https:// address.
One must specify the model used at the endpoint so the prompt type is handled. This assumes that base model is specified in prompter.py::prompt_type_to_model_name. Otherwise, one should pass --prompt_type as well, like:
python generate.py --inference_server="http://192.168.0.10:7680" --base_model=foo_model --prompt_type=wizard2
If even prompt_type is not listed in enums.py::PromptType then one can pass --prompt_dict like:
python generate.py --inference_server="http://192.168.0.10:7680" --base_model=foo_model --prompt_type=custom --prompt_dict="{'PreInput': None,'PreInstruct': '', 'PreResponse': '<bot>:', 'botstr': '<bot>:', 'chat_sep': '\n', 'humanstr': '<human>:', 'promptA': '<human>: ', 'promptB': '<human>: ', 'terminate_response': ['<human>:', '<bot>:']}"
which is just an example for the human_bot prompt type.
OpenAI Inference Server-Client
If you have an OpenAI key and set an ENV OPENAI_API_KEY, then you can access OpenAI models via gradio by running:
OPENAI_API_KEY=<key> python generate.py --inference_server="openai_chat" --base_model=gpt-3.5-turbo --h2ocolors=False --langchain_mode=MyData
where <key> should be replaced by your OpenAI key that probably starts with sk-. OpenAI is not recommended for private document question-answer, but it can be a good reference for testing purposes or when privacy is not required.
h2oGPT start-up vs. in-app selection
When using generate.py, specifying the --base_model or --inference_server on the CLI is not required. One can also add any model and server URL (with optional port) in the Model tab at the bottom:
Enter the mode name as the same name one would use for --base_model and enter the server url:port as the same url (optional port) one would use for --inference_server. Then click Add new Model, Lora, Server url:port button. This adds that to the drop-down selection, and then one can load the model by clicking "Load-Unload" model button. For an inference server, the Load 8-bit, Choose Devices, LORA, and GPU ID buttons or selections are not applicable.
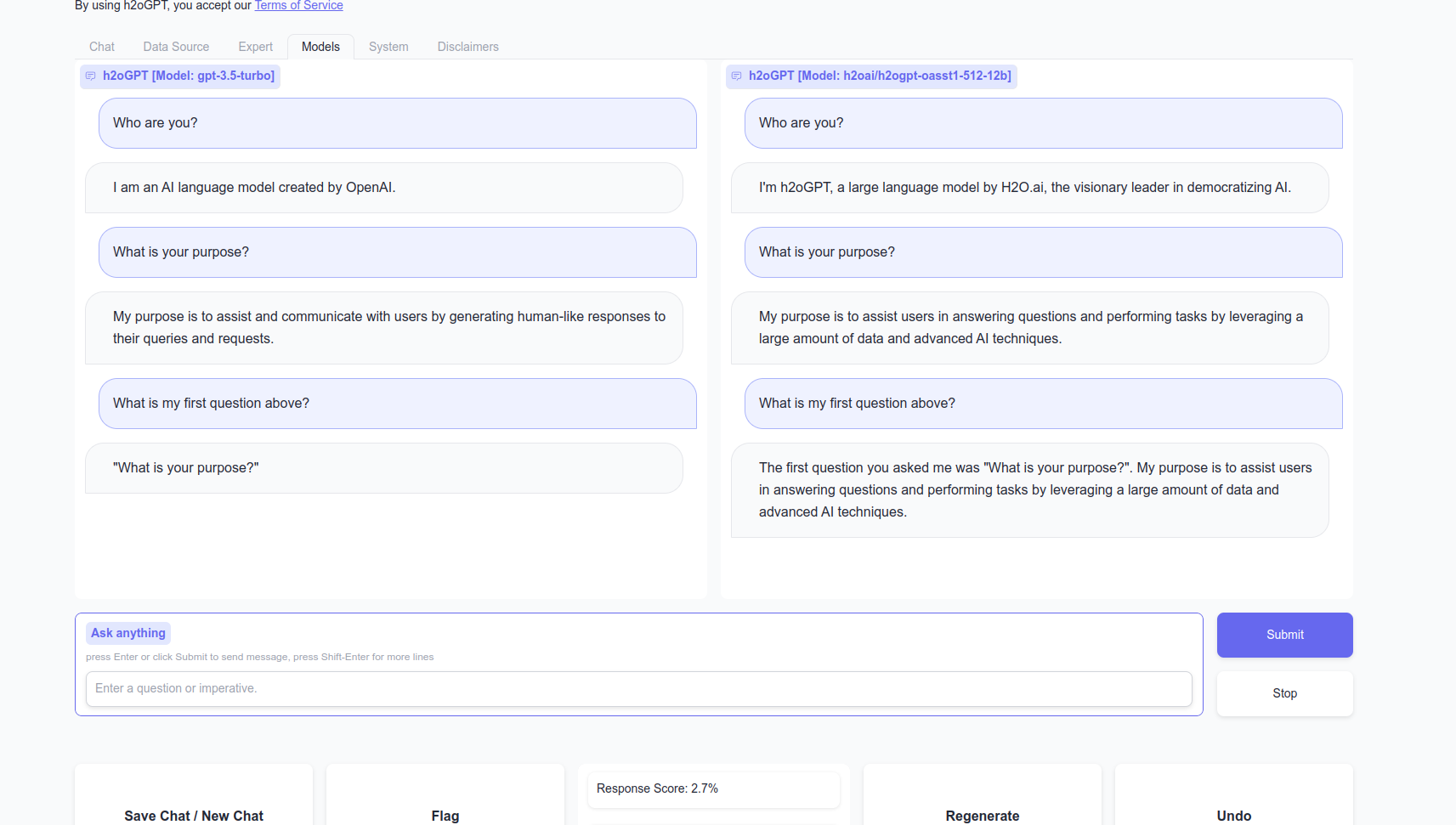
One can also do model comparison by clicking the Compare Mode checkbox, and add new models and servers to each left and right models for a view like:
Locking Models for easy start-up or in-app comparison
To avoid specifying model-related settings as independent options, and to disable loading new models, use --model_lock like:
python generate.py --model_lock=[{'inference_server':'http://192.168.1.46:6112','base_model':'h2oai/h2ogpt-oasst1-512-12b'}]
where for this case the prompt_type for this base_model is in prompter.py, so it doesn't need to be specified. Note that no spaces or other white space is allowed within the double quotes for model_lock due to how CLI arguments are parsed. For two endpoints, one uses (again with no spaces in arg)
python generate.py --model_lock=[{'inference_server':'http://192.168.1.46:6112','base_model':'h2oai/h2ogpt-oasst1-512-12b'},{'inference_server':'http://192.168.1.46:6114','base_model':'h2oai/h2ogpt-oasst1-512-20b'},{'inference_server':'http://192.168.1.46:6113','base_model':'h2oai/h2ogpt-gm-oasst1-en-2048-falcon-7b-v2'}]
One can have a mix of local models, HF text-generation inference servers, Gradio generation servers, and OpenAI servers, e.g.:
python generate.py --model_lock=[{'inference_server':'http://192.168.1.46:6112','base_model':'h2oai/h2ogpt-oasst1-512-12b'},{'inference_server':'http://192.168.1.46:6114','base_model':'h2oai/h2ogpt-oasst1-512-20b'},{'inference_server':'http://192.168.1.46:6113','base_model':'h2oai/h2ogpt-gm-oasst1-en-2048-falcon-7b-v2'},{'inference_server':'http://192.168.0.1:6000','base_model':'TheBloke/Wizard-Vicuna-13B-Uncensored-HF','prompt_type':'instruct_vicuna'},{'inference_server':'http://192.168.0.245:6000','base_model':'h2oai/h2ogpt-oasst1-falcon-40b'},{'inference_server':'http://192.168.1.46:7860','base_model':'h2oai/h2ogpt-oasst1-512-12b'},{'inference_server':'http://192.168.0.1:7000','base_model':'h2oai/h2ogpt-research-oasst1-llama-65b','prompt_type':'human_bot'},{'inference_server':'openai_chat','base_model':'gpt-3.5-turbo'}] --model_lock_columns=4
where the lock columns of 4 makes a grid of chatbots with 4 columns.
If you run in bash and need to use an authentication for the Hugging Face text generation inference server, then that can be passed:
{'inference_server':'https://server.h2o.ai USER AUTH','base_model':'h2oai/h2ogpt-gm-oasst1-en-2048-falcon-7b-v2'}
i.e. 4 spaces between each IP, USER, and AUTH. USER should be the user and AUTH be the token.
When bringing up generate.py with any inference server, one can set REQUEST_TIMEOUT ENV to smaller value than default of 60 seconds to get server up faster if one has many inaccessible endpoints you don't mind skipping. E.g. set REQUEST_TIMEOUT=5. One can also choose the timeout overall for each chat turn using env REQUEST_TIMEOUT_FAST that defaults to 10 seconds.
Note: The client API calls for chat APIs (i.e. instruction type for instruction, instruction_bot, instruction_bot_score, and similar for submit and retry types) require managing all chat sessions via API. However, the nochat APIs only use the first model in the list of chats or model_lock list.
System info from gradio server
import json
from gradio_client import Client
ADMIN_PASS = ''
HOST = "http://localhost:7860"
client = Client(HOST)
api_name = '/system_info_dict'
res = client.predict(ADMIN_PASS, api_name=api_name)
res = json.loads(res)
print(res)
# e.g.
print(res['base_model'])
print(res['hash'])
where one should set ADMIN_PASS to pass set for that instance and change HOST to the desired host.