BEiT
Overview
BEiT モデルは、BEiT: BERT Pre-Training of Image Transformers で提案されました。 ハンボ・バオ、リー・ドン、フル・ウェイ。 BERT に触発された BEiT は、自己教師ありの事前トレーニングを作成した最初の論文です。 ビジョン トランスフォーマー (ViT) は、教師付き事前トレーニングよりも優れたパフォーマンスを発揮します。クラスを予測するためにモデルを事前トレーニングするのではなく (オリジナルの ViT 論文 で行われたように) 画像の BEiT モデルは、次のように事前トレーニングされています。 マスクされた OpenAI の DALL-E モデル のコードブックからビジュアル トークンを予測します パッチ。
論文の要約は次のとおりです。
自己教師あり視覚表現モデル BEiT (Bidirectional Encoderpresentation) を導入します。 イメージトランスフォーマーより。自然言語処理分野で開発されたBERTに倣い、マスク画像を提案します。 ビジョントランスフォーマーを事前にトレーニングするためのモデリングタスク。具体的には、事前トレーニングでは各画像に 2 つのビューがあります。 パッチ (16x16 ピクセルなど)、およびビジュアル トークン (つまり、個別のトークン)。まず、元の画像を「トークン化」して、 ビジュアルトークン。次に、いくつかの画像パッチをランダムにマスクし、それらをバックボーンの Transformer に供給します。事前トレーニング 目的は、破損したイメージ パッチに基づいて元のビジュアル トークンを回復することです。 BEiTの事前トレーニング後、 事前トレーニングされたエンコーダーにタスク レイヤーを追加することで、ダウンストリーム タスクのモデル パラメーターを直接微調整します。 画像分類とセマンティックセグメンテーションに関する実験結果は、私たちのモデルが競争力のある結果を達成することを示しています 以前の事前トレーニング方法を使用して。たとえば、基本サイズの BEiT は、ImageNet-1K で 83.2% のトップ 1 精度を達成します。 同じ設定でゼロからの DeiT トレーニング (81.8%) を大幅に上回りました。また、大型BEiTは 86.3% は ImageNet-1K のみを使用しており、ImageNet-22K での教師付き事前トレーニングを使用した ViT-L (85.2%) を上回っています。
Usage tips
- BEiT モデルは通常のビジョン トランスフォーマーですが、教師ありではなく自己教師ありの方法で事前トレーニングされています。彼らは
ImageNet-1K および CIFAR-100 で微調整すると、オリジナル モデル (ViT) と データ効率の高いイメージ トランスフォーマー (DeiT) の両方を上回るパフォーマンスを発揮します。推論に関するデモノートブックもチェックできます。
カスタム データの微調整は こちら (置き換えるだけで済みます)
BeitImageProcessor による
ViTFeatureExtractorとViTForImageClassificationby BeitForImageClassification)。 - DALL-E の画像トークナイザーと BEiT を組み合わせる方法を紹介するデモ ノートブックも利用可能です。 マスクされた画像モデリングを実行します。 ここ で見つけることができます。
- BEiT モデルは各画像が同じサイズ (解像度) であることを期待しているため、次のように使用できます。 BeitImageProcessor を使用して、モデルの画像のサイズを変更 (または再スケール) し、正規化します。
- 事前トレーニングまたは微調整中に使用されるパッチ解像度と画像解像度の両方が名前に反映されます。
各チェックポイント。たとえば、
microsoft/beit-base-patch16-224は、パッチ付きの基本サイズのアーキテクチャを指します。 解像度は 16x16、微調整解像度は 224x224 です。すべてのチェックポイントは ハブ で見つけることができます。 - 利用可能なチェックポイントは、(1) ImageNet-22k で事前トレーニングされています ( 1,400 万の画像と 22,000 のクラス) のみ、(2) ImageNet-22k でも微調整、または (3) ImageNet-1kでも微調整/2012/) (ILSVRC 2012 とも呼ばれ、130 万件のコレクション) 画像と 1,000 クラス)。
- BEiT は、T5 モデルからインスピレーションを得た相対位置埋め込みを使用します。事前トレーニング中に、著者は次のことを共有しました。
いくつかの自己注意層間の相対的な位置の偏り。微調整中、各レイヤーの相対位置
バイアスは、事前トレーニング後に取得された共有相対位置バイアスで初期化されます。ご希望の場合は、
モデルを最初から事前トレーニングするには、
use_relative_position_biasまたは 追加するには、BeitConfig のuse_relative_position_bias属性をTrueに設定します。 位置の埋め込み。
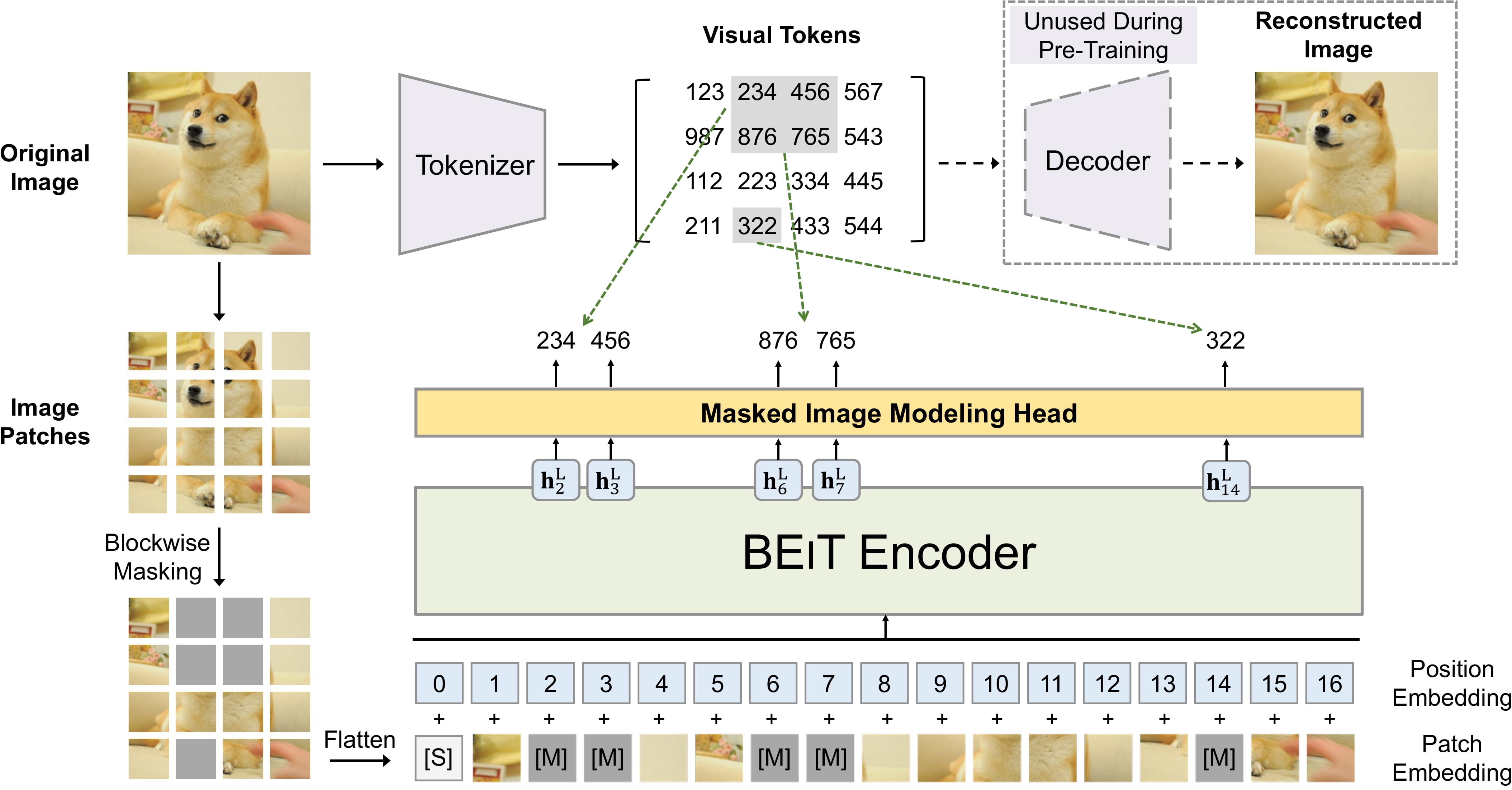 BEiT の事前トレーニング。 元の論文から抜粋。
BEiT の事前トレーニング。 元の論文から抜粋。 このモデルは、nielsr によって提供されました。このモデルの JAX/FLAX バージョンは、 kamalkraj による投稿。元のコードは ここ にあります。
Resources
BEiT の使用を開始するのに役立つ公式 Hugging Face およびコミュニティ (🌎 で示されている) リソースのリスト。
- BeitForImageClassification は、この サンプル スクリプト および ノートブック。
- 参照: 画像分類タスク ガイド
セマンティック セグメンテーション
ここに含めるリソースの送信に興味がある場合は、お気軽にプル リクエストを開いてください。審査させていただきます。リソースは、既存のリソースを複製するのではなく、何か新しいものを示すことが理想的です。
BEiT specific outputs
class transformers.models.beit.modeling_beit.BeitModelOutputWithPooling
< source >( last_hidden_state: FloatTensor = None pooler_output: FloatTensor = None hidden_states: Optional = None attentions: Optional = None )
Parameters
- last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)) — Sequence of hidden-states at the output of the last layer of the model. - pooler_output (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, hidden_size)) — Average of the last layer hidden states of the patch tokens (excluding the [CLS] token) if config.use_mean_pooling is set to True. If set to False, then the final hidden state of the [CLS] token will be returned. - hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the initial embedding outputs.
- attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length).Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
Class for outputs of BeitModel.
class transformers.models.beit.modeling_flax_beit.FlaxBeitModelOutputWithPooling
< source >( last_hidden_state: Array = None pooler_output: Array = None hidden_states: Optional = None attentions: Optional = None )
Parameters
- last_hidden_state (
jnp.ndarrayof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)) — Sequence of hidden-states at the output of the last layer of the model. - pooler_output (
jnp.ndarrayof shape(batch_size, hidden_size)) — Average of the last layer hidden states of the patch tokens (excluding the [CLS] token) if config.use_mean_pooling is set to True. If set to False, then the final hidden state of the [CLS] token will be returned. - hidden_states (
tuple(jnp.ndarray), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple ofjnp.ndarray(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size). Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the initial embedding outputs. - attentions (
tuple(jnp.ndarray), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple ofjnp.ndarray(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length). Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
Class for outputs of FlaxBeitModel.
BeitConfig
class transformers.BeitConfig
< source >( vocab_size = 8192 hidden_size = 768 num_hidden_layers = 12 num_attention_heads = 12 intermediate_size = 3072 hidden_act = 'gelu' hidden_dropout_prob = 0.0 attention_probs_dropout_prob = 0.0 initializer_range = 0.02 layer_norm_eps = 1e-12 image_size = 224 patch_size = 16 num_channels = 3 use_mask_token = False use_absolute_position_embeddings = False use_relative_position_bias = False use_shared_relative_position_bias = False layer_scale_init_value = 0.1 drop_path_rate = 0.1 use_mean_pooling = True pool_scales = [1, 2, 3, 6] use_auxiliary_head = True auxiliary_loss_weight = 0.4 auxiliary_channels = 256 auxiliary_num_convs = 1 auxiliary_concat_input = False semantic_loss_ignore_index = 255 out_features = None out_indices = None add_fpn = False reshape_hidden_states = True **kwargs )
Parameters
- vocab_size (
int, optional, defaults to 8192) — Vocabulary size of the BEiT model. Defines the number of different image tokens that can be used during pre-training. - hidden_size (
int, optional, defaults to 768) — Dimensionality of the encoder layers and the pooler layer. - num_hidden_layers (
int, optional, defaults to 12) — Number of hidden layers in the Transformer encoder. - num_attention_heads (
int, optional, defaults to 12) — Number of attention heads for each attention layer in the Transformer encoder. - intermediate_size (
int, optional, defaults to 3072) — Dimensionality of the “intermediate” (i.e., feed-forward) layer in the Transformer encoder. - hidden_act (
strorfunction, optional, defaults to"gelu") — The non-linear activation function (function or string) in the encoder and pooler. If string,"gelu","relu","selu"and"gelu_new"are supported. - hidden_dropout_prob (
float, optional, defaults to 0.0) — The dropout probability for all fully connected layers in the embeddings, encoder, and pooler. - attention_probs_dropout_prob (
float, optional, defaults to 0.0) — The dropout ratio for the attention probabilities. - initializer_range (
float, optional, defaults to 0.02) — The standard deviation of the truncated_normal_initializer for initializing all weight matrices. - layer_norm_eps (
float, optional, defaults to 1e-12) — The epsilon used by the layer normalization layers. - image_size (
int, optional, defaults to 224) — The size (resolution) of each image. - patch_size (
int, optional, defaults to 16) — The size (resolution) of each patch. - num_channels (
int, optional, defaults to 3) — The number of input channels. - use_mask_token (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether to use a mask token for masked image modeling. - use_absolute_position_embeddings (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether to use BERT-style absolute position embeddings. - use_relative_position_bias (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether to use T5-style relative position embeddings in the self-attention layers. - use_shared_relative_position_bias (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether to use the same relative position embeddings across all self-attention layers of the Transformer. - layer_scale_init_value (
float, optional, defaults to 0.1) — Scale to use in the self-attention layers. 0.1 for base, 1e-5 for large. Set 0 to disable layer scale. - drop_path_rate (
float, optional, defaults to 0.1) — Stochastic depth rate per sample (when applied in the main path of residual layers). - use_mean_pooling (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to mean pool the final hidden states of the patches instead of using the final hidden state of the CLS token, before applying the classification head. - pool_scales (
Tuple[int], optional, defaults to[1, 2, 3, 6]) — Pooling scales used in Pooling Pyramid Module applied on the last feature map. - use_auxiliary_head (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to use an auxiliary head during training. - auxiliary_loss_weight (
float, optional, defaults to 0.4) — Weight of the cross-entropy loss of the auxiliary head. - auxiliary_channels (
int, optional, defaults to 256) — Number of channels to use in the auxiliary head. - auxiliary_num_convs (
int, optional, defaults to 1) — Number of convolutional layers to use in the auxiliary head. - auxiliary_concat_input (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether to concatenate the output of the auxiliary head with the input before the classification layer. - semantic_loss_ignore_index (
int, optional, defaults to 255) — The index that is ignored by the loss function of the semantic segmentation model. - out_features (
List[str], optional) — If used as backbone, list of features to output. Can be any of"stem","stage1","stage2", etc. (depending on how many stages the model has). If unset andout_indicesis set, will default to the corresponding stages. If unset andout_indicesis unset, will default to the last stage. Must be in the same order as defined in thestage_namesattribute. - out_indices (
List[int], optional) — If used as backbone, list of indices of features to output. Can be any of 0, 1, 2, etc. (depending on how many stages the model has). If unset andout_featuresis set, will default to the corresponding stages. If unset andout_featuresis unset, will default to the last stage. Must be in the same order as defined in thestage_namesattribute. - add_fpn (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether to add a FPN as part of the backbone. Only relevant forBeitBackbone. - reshape_hidden_states (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to reshape the feature maps to 4D tensors of shape(batch_size, hidden_size, height, width)in case the model is used as backbone. IfFalse, the feature maps will be 3D tensors of shape(batch_size, seq_len, hidden_size). Only relevant forBeitBackbone.
This is the configuration class to store the configuration of a BeitModel. It is used to instantiate an BEiT model according to the specified arguments, defining the model architecture. Instantiating a configuration with the defaults will yield a similar configuration to that of the BEiT microsoft/beit-base-patch16-224-pt22k architecture.
Example:
>>> from transformers import BeitConfig, BeitModel
>>> # Initializing a BEiT beit-base-patch16-224-pt22k style configuration
>>> configuration = BeitConfig()
>>> # Initializing a model (with random weights) from the beit-base-patch16-224-pt22k style configuration
>>> model = BeitModel(configuration)
>>> # Accessing the model configuration
>>> configuration = model.configBeitFeatureExtractor
post_process_semantic_segmentation
< source >( outputs target_sizes: List = None ) → semantic_segmentation
Parameters
- outputs (BeitForSemanticSegmentation) — Raw outputs of the model.
- target_sizes (
List[Tuple]of lengthbatch_size, optional) — List of tuples corresponding to the requested final size (height, width) of each prediction. If unset, predictions will not be resized.
Returns
semantic_segmentation
List[torch.Tensor] of length batch_size, where each item is a semantic
segmentation map of shape (height, width) corresponding to the target_sizes entry (if target_sizes is
specified). Each entry of each torch.Tensor correspond to a semantic class id.
Converts the output of BeitForSemanticSegmentation into semantic segmentation maps. Only supports PyTorch.
BeitImageProcessor
class transformers.BeitImageProcessor
< source >( do_resize: bool = True size: Dict = None resample: Resampling = <Resampling.BICUBIC: 3> do_center_crop: bool = True crop_size: Dict = None rescale_factor: Union = 0.00392156862745098 do_rescale: bool = True do_normalize: bool = True image_mean: Union = None image_std: Union = None do_reduce_labels: bool = False **kwargs )
Parameters
- do_resize (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to resize the image’s (height, width) dimensions to the specifiedsize. Can be overridden by thedo_resizeparameter in thepreprocessmethod. - size (
Dict[str, int]optional, defaults to{"height" -- 256, "width": 256}): Size of the output image after resizing. Can be overridden by thesizeparameter in thepreprocessmethod. - resample (
PILImageResampling, optional, defaults toResampling.BICUBIC) — Resampling filter to use if resizing the image. Can be overridden by theresampleparameter in thepreprocessmethod. - do_center_crop (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to center crop the image. If the input size is smaller thancrop_sizealong any edge, the image is padded with 0’s and then center cropped. Can be overridden by thedo_center_cropparameter in thepreprocessmethod. - crop_size (
Dict[str, int], optional, defaults to{"height" -- 224, "width": 224}): Desired output size when applying center-cropping. Only has an effect ifdo_center_cropis set toTrue. Can be overridden by thecrop_sizeparameter in thepreprocessmethod. - rescale_factor (
intorfloat, optional, defaults to1/255) — Scale factor to use if rescaling the image. Can be overridden by therescale_factorparameter in thepreprocessmethod. - do_rescale (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to rescale the image by the specified scalerescale_factor. Can be overridden by thedo_rescaleparameter in thepreprocessmethod. - do_normalize (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to normalize the image. Can be overridden by thedo_normalizeparameter in thepreprocessmethod. - image_mean (
floatorList[float], optional, defaults toIMAGENET_STANDARD_MEAN) — The mean to use if normalizing the image. This is a float or list of floats of length of the number of channels of the image. Can be overridden by theimage_meanparameter in thepreprocessmethod. - image_std (
floatorList[float], optional, defaults toIMAGENET_STANDARD_STD) — The standard deviation to use if normalizing the image. This is a float or list of floats of length of the number of channels of the image. Can be overridden by theimage_stdparameter in thepreprocessmethod. - do_reduce_labels (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether or not to reduce all label values of segmentation maps by 1. Usually used for datasets where 0 is used for background, and background itself is not included in all classes of a dataset (e.g. ADE20k). The background label will be replaced by 255. Can be overridden by thedo_reduce_labelsparameter in thepreprocessmethod.
Constructs a BEiT image processor.
preprocess
< source >( images: Union segmentation_maps: Union = None do_resize: bool = None size: Dict = None resample: Resampling = None do_center_crop: bool = None crop_size: Dict = None do_rescale: bool = None rescale_factor: float = None do_normalize: bool = None image_mean: Union = None image_std: Union = None do_reduce_labels: Optional = None return_tensors: Union = None data_format: ChannelDimension = <ChannelDimension.FIRST: 'channels_first'> input_data_format: Union = None )
Parameters
- images (
ImageInput) — Image to preprocess. Expects a single or batch of images with pixel values ranging from 0 to 255. If passing in images with pixel values between 0 and 1, setdo_rescale=False. - segmentation_maps (
ImageInput, optional) — Segmentation maps to preprocess. Expects a single or batch of images with pixel values ranging from 0 to 255. If passing in images with pixel values between 0 and 1, setdo_rescale=False. - do_resize (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_resize) — Whether to resize the image. - size (
Dict[str, int], optional, defaults toself.size) — Size of the image after resizing. - resample (
int, optional, defaults toself.resample) — Resampling filter to use if resizing the image. This can be one of the enumPILImageResampling, Only has an effect ifdo_resizeis set toTrue. - do_center_crop (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_center_crop) — Whether to center crop the image. - crop_size (
Dict[str, int], optional, defaults toself.crop_size) — Size of the image after center crop. If one edge the image is smaller thancrop_size, it will be padded with zeros and then cropped - do_rescale (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_rescale) — Whether to rescale the image values between [0 - 1]. - rescale_factor (
float, optional, defaults toself.rescale_factor) — Rescale factor to rescale the image by ifdo_rescaleis set toTrue. - do_normalize (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_normalize) — Whether to normalize the image. - image_mean (
floatorList[float], optional, defaults toself.image_mean) — Image mean. - image_std (
floatorList[float], optional, defaults toself.image_std) — Image standard deviation. - do_reduce_labels (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_reduce_labels) — Whether or not to reduce all label values of segmentation maps by 1. Usually used for datasets where 0 is used for background, and background itself is not included in all classes of a dataset (e.g. ADE20k). The background label will be replaced by 255. - return_tensors (
strorTensorType, optional) — The type of tensors to return. Can be one of:- Unset: Return a list of
np.ndarray. TensorType.TENSORFLOWor'tf': Return a batch of typetf.Tensor.TensorType.PYTORCHor'pt': Return a batch of typetorch.Tensor.TensorType.NUMPYor'np': Return a batch of typenp.ndarray.TensorType.JAXor'jax': Return a batch of typejax.numpy.ndarray.
- Unset: Return a list of
- data_format (
ChannelDimensionorstr, optional, defaults toChannelDimension.FIRST) — The channel dimension format for the output image. Can be one of:"channels_first"orChannelDimension.FIRST: image in (num_channels, height, width) format."channels_last"orChannelDimension.LAST: image in (height, width, num_channels) format.- Unset: Use the channel dimension format of the input image.
- input_data_format (
ChannelDimensionorstr, optional) — The channel dimension format for the input image. If unset, the channel dimension format is inferred from the input image. Can be one of:"channels_first"orChannelDimension.FIRST: image in (num_channels, height, width) format."channels_last"orChannelDimension.LAST: image in (height, width, num_channels) format."none"orChannelDimension.NONE: image in (height, width) format.
Preprocess an image or batch of images.
post_process_semantic_segmentation
< source >( outputs target_sizes: List = None ) → semantic_segmentation
Parameters
- outputs (BeitForSemanticSegmentation) — Raw outputs of the model.
- target_sizes (
List[Tuple]of lengthbatch_size, optional) — List of tuples corresponding to the requested final size (height, width) of each prediction. If unset, predictions will not be resized.
Returns
semantic_segmentation
List[torch.Tensor] of length batch_size, where each item is a semantic
segmentation map of shape (height, width) corresponding to the target_sizes entry (if target_sizes is
specified). Each entry of each torch.Tensor correspond to a semantic class id.
Converts the output of BeitForSemanticSegmentation into semantic segmentation maps. Only supports PyTorch.
BeitModel
class transformers.BeitModel
< source >( config: BeitConfig add_pooling_layer: bool = True )
Parameters
- config (BeitConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
The bare Beit Model transformer outputting raw hidden-states without any specific head on top. This model is a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
< source >( pixel_values: Tensor bool_masked_pos: Optional = None head_mask: Optional = None output_attentions: Optional = None output_hidden_states: Optional = None interpolate_pos_encoding: bool = False return_dict: Optional = None ) → transformers.models.beit.modeling_beit.BeitModelOutputWithPooling or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. Pixel values can be obtained using AutoImageProcessor. See BeitImageProcessor.call() for details. - head_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(num_heads,)or(num_layers, num_heads), optional) — Mask to nullify selected heads of the self-attention modules. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 indicates the head is not masked,
- 0 indicates the head is masked.
- output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail. - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail. - interpolate_pos_encoding (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether to interpolate the pre-trained position encodings. - return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple. - bool_masked_pos (
torch.BoolTensorof shape(batch_size, num_patches), optional) — Boolean masked positions. Indicates which patches are masked (1) and which aren’t (0).
Returns
transformers.models.beit.modeling_beit.BeitModelOutputWithPooling or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.models.beit.modeling_beit.BeitModelOutputWithPooling or a tuple of
torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various
elements depending on the configuration (BeitConfig) and inputs.
-
last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)) — Sequence of hidden-states at the output of the last layer of the model. -
pooler_output (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, hidden_size)) — Average of the last layer hidden states of the patch tokens (excluding the [CLS] token) if config.use_mean_pooling is set to True. If set to False, then the final hidden state of the [CLS] token will be returned. -
hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the initial embedding outputs.
-
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length).Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
The BeitModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module
instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while
the latter silently ignores them.
Example:
>>> from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, BeitModel
>>> import torch
>>> from datasets import load_dataset
>>> dataset = load_dataset("huggingface/cats-image", trust_remote_code=True)
>>> image = dataset["test"]["image"][0]
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("microsoft/beit-base-patch16-224-pt22k")
>>> model = BeitModel.from_pretrained("microsoft/beit-base-patch16-224-pt22k")
>>> inputs = image_processor(image, return_tensors="pt")
>>> with torch.no_grad():
... outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> last_hidden_states = outputs.last_hidden_state
>>> list(last_hidden_states.shape)
[1, 197, 768]BeitForMaskedImageModeling
class transformers.BeitForMaskedImageModeling
< source >( config: BeitConfig )
Parameters
- config (BeitConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
Beit Model transformer with a ‘language’ modeling head on top. BEiT does masked image modeling by predicting visual tokens of a Vector-Quantize Variational Autoencoder (VQ-VAE), whereas other vision models like ViT and DeiT predict RGB pixel values. As a result, this class is incompatible with AutoModelForMaskedImageModeling, so you will need to use BeitForMaskedImageModeling directly if you wish to do masked image modeling with BEiT. This model is a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
< source >( pixel_values: Optional = None bool_masked_pos: Optional = None head_mask: Optional = None labels: Optional = None output_attentions: Optional = None output_hidden_states: Optional = None interpolate_pos_encoding: bool = False return_dict: Optional = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.MaskedLMOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. Pixel values can be obtained using AutoImageProcessor. See BeitImageProcessor.call() for details. - head_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(num_heads,)or(num_layers, num_heads), optional) — Mask to nullify selected heads of the self-attention modules. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 indicates the head is not masked,
- 0 indicates the head is masked.
- output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail. - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail. - interpolate_pos_encoding (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether to interpolate the pre-trained position encodings. - return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple. - bool_masked_pos (
torch.BoolTensorof shape(batch_size, num_patches)) — Boolean masked positions. Indicates which patches are masked (1) and which aren’t (0). - labels (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size,), optional) — Labels for computing the image classification/regression loss. Indices should be in[0, ..., config.num_labels - 1]. Ifconfig.num_labels == 1a regression loss is computed (Mean-Square loss), Ifconfig.num_labels > 1a classification loss is computed (Cross-Entropy).
Returns
transformers.modeling_outputs.MaskedLMOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.modeling_outputs.MaskedLMOutput or a tuple of
torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various
elements depending on the configuration (BeitConfig) and inputs.
-
loss (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(1,), optional, returned whenlabelsis provided) — Masked language modeling (MLM) loss. -
logits (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, config.vocab_size)) — Prediction scores of the language modeling head (scores for each vocabulary token before SoftMax). -
hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the optional initial embedding outputs.
-
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length).Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
The BeitForMaskedImageModeling forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module
instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while
the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
>>> from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, BeitForMaskedImageModeling
>>> import torch
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> import requests
>>> url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
>>> image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("microsoft/beit-base-patch16-224-pt22k")
>>> model = BeitForMaskedImageModeling.from_pretrained("microsoft/beit-base-patch16-224-pt22k")
>>> num_patches = (model.config.image_size // model.config.patch_size) ** 2
>>> pixel_values = image_processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt").pixel_values
>>> # create random boolean mask of shape (batch_size, num_patches)
>>> bool_masked_pos = torch.randint(low=0, high=2, size=(1, num_patches)).bool()
>>> outputs = model(pixel_values, bool_masked_pos=bool_masked_pos)
>>> loss, logits = outputs.loss, outputs.logits
>>> list(logits.shape)
[1, 196, 8192]BeitForImageClassification
class transformers.BeitForImageClassification
< source >( config: BeitConfig )
Parameters
- config (BeitConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
Beit Model transformer with an image classification head on top (a linear layer on top of the average of the final hidden states of the patch tokens) e.g. for ImageNet.
This model is a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
< source >( pixel_values: Optional = None head_mask: Optional = None labels: Optional = None output_attentions: Optional = None output_hidden_states: Optional = None interpolate_pos_encoding: bool = False return_dict: Optional = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.ImageClassifierOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. Pixel values can be obtained using AutoImageProcessor. See BeitImageProcessor.call() for details. - head_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(num_heads,)or(num_layers, num_heads), optional) — Mask to nullify selected heads of the self-attention modules. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 indicates the head is not masked,
- 0 indicates the head is masked.
- output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail. - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail. - interpolate_pos_encoding (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether to interpolate the pre-trained position encodings. - return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple. - labels (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size,), optional) — Labels for computing the image classification/regression loss. Indices should be in[0, ..., config.num_labels - 1]. Ifconfig.num_labels == 1a regression loss is computed (Mean-Square loss), Ifconfig.num_labels > 1a classification loss is computed (Cross-Entropy).
Returns
transformers.modeling_outputs.ImageClassifierOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.modeling_outputs.ImageClassifierOutput or a tuple of
torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various
elements depending on the configuration (BeitConfig) and inputs.
-
loss (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(1,), optional, returned whenlabelsis provided) — Classification (or regression if config.num_labels==1) loss. -
logits (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, config.num_labels)) — Classification (or regression if config.num_labels==1) scores (before SoftMax). -
hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, + one for the output of each stage) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size). Hidden-states (also called feature maps) of the model at the output of each stage. -
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, patch_size, sequence_length).Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
The BeitForImageClassification forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module
instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while
the latter silently ignores them.
Example:
>>> from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, BeitForImageClassification
>>> import torch
>>> from datasets import load_dataset
>>> dataset = load_dataset("huggingface/cats-image", trust_remote_code=True)
>>> image = dataset["test"]["image"][0]
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("microsoft/beit-base-patch16-224")
>>> model = BeitForImageClassification.from_pretrained("microsoft/beit-base-patch16-224")
>>> inputs = image_processor(image, return_tensors="pt")
>>> with torch.no_grad():
... logits = model(**inputs).logits
>>> # model predicts one of the 1000 ImageNet classes
>>> predicted_label = logits.argmax(-1).item()
>>> print(model.config.id2label[predicted_label])
tabby, tabby catBeitForSemanticSegmentation
class transformers.BeitForSemanticSegmentation
< source >( config: BeitConfig )
Parameters
- config (BeitConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
Beit Model transformer with a semantic segmentation head on top e.g. for ADE20k, CityScapes.
This model is a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
< source >( pixel_values: Optional = None head_mask: Optional = None labels: Optional = None output_attentions: Optional = None output_hidden_states: Optional = None interpolate_pos_encoding: bool = False return_dict: Optional = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.SemanticSegmenterOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Pixel values. Pixel values can be obtained using AutoImageProcessor. See BeitImageProcessor.call() for details. - head_mask (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(num_heads,)or(num_layers, num_heads), optional) — Mask to nullify selected heads of the self-attention modules. Mask values selected in[0, 1]:- 1 indicates the head is not masked,
- 0 indicates the head is masked.
- output_attentions (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. Seeattentionsunder returned tensors for more detail. - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail. - interpolate_pos_encoding (
bool, optional, defaults toFalse) — Whether to interpolate the pre-trained position encodings. - return_dict (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return a ModelOutput instead of a plain tuple. - labels (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size, height, width), optional) — Ground truth semantic segmentation maps for computing the loss. Indices should be in[0, ..., config.num_labels - 1]. Ifconfig.num_labels > 1, a classification loss is computed (Cross-Entropy).
Returns
transformers.modeling_outputs.SemanticSegmenterOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.modeling_outputs.SemanticSegmenterOutput or a tuple of
torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various
elements depending on the configuration (BeitConfig) and inputs.
-
loss (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(1,), optional, returned whenlabelsis provided) — Classification (or regression if config.num_labels==1) loss. -
logits (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, config.num_labels, logits_height, logits_width)) — Classification scores for each pixel.The logits returned do not necessarily have the same size as the
pixel_valuespassed as inputs. This is to avoid doing two interpolations and lose some quality when a user needs to resize the logits to the original image size as post-processing. You should always check your logits shape and resize as needed. -
hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, patch_size, hidden_size).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the optional initial embedding outputs.
-
attentions (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, patch_size, sequence_length).Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
The BeitForSemanticSegmentation forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module
instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while
the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
>>> from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, BeitForSemanticSegmentation
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> import requests
>>> url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
>>> image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("microsoft/beit-base-finetuned-ade-640-640")
>>> model = BeitForSemanticSegmentation.from_pretrained("microsoft/beit-base-finetuned-ade-640-640")
>>> inputs = image_processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt")
>>> outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> # logits are of shape (batch_size, num_labels, height, width)
>>> logits = outputs.logitsFlaxBeitModel
class transformers.FlaxBeitModel
< source >( config: BeitConfig input_shape = None seed: int = 0 dtype: dtype = <class 'jax.numpy.float32'> _do_init: bool = True **kwargs )
Parameters
- config (BeitConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
- dtype (
jax.numpy.dtype, optional, defaults tojax.numpy.float32) — The data type of the computation. Can be one ofjax.numpy.float32,jax.numpy.float16(on GPUs) andjax.numpy.bfloat16(on TPUs).This can be used to enable mixed-precision training or half-precision inference on GPUs or TPUs. If specified all the computation will be performed with the given
dtype.Note that this only specifies the dtype of the computation and does not influence the dtype of model parameters.
If you wish to change the dtype of the model parameters, see to_fp16() and to_bf16().
The bare Beit Model transformer outputting raw hidden-states without any specific head on top.
This model inherits from FlaxPreTrainedModel. Check the superclass documentation for the generic methods the library implements for all its model (such as downloading, saving and converting weights from PyTorch models)
This model is also a flax.linen.Module subclass. Use it as a regular Flax linen Module and refer to the Flax documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
Finally, this model supports inherent JAX features such as:
__call__
< source >( pixel_values bool_masked_pos = None params: dict = None dropout_rng: PRNGKey = None train: bool = False output_attentions: Optional = None output_hidden_states: Optional = None return_dict: Optional = None ) → transformers.models.beit.modeling_flax_beit.FlaxBeitModelOutputWithPooling or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Returns
transformers.models.beit.modeling_flax_beit.FlaxBeitModelOutputWithPooling or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.models.beit.modeling_flax_beit.FlaxBeitModelOutputWithPooling or a tuple of
torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various
elements depending on the configuration (<class 'transformers.models.beit.configuration_beit.BeitConfig'>) and inputs.
- last_hidden_state (
jnp.ndarrayof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)) — Sequence of hidden-states at the output of the last layer of the model. - pooler_output (
jnp.ndarrayof shape(batch_size, hidden_size)) — Average of the last layer hidden states of the patch tokens (excluding the [CLS] token) if config.use_mean_pooling is set to True. If set to False, then the final hidden state of the [CLS] token will be returned. - hidden_states (
tuple(jnp.ndarray), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple ofjnp.ndarray(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size). Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the initial embedding outputs. - attentions (
tuple(jnp.ndarray), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple ofjnp.ndarray(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length). Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
The FlaxBeitPreTrainedModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module
instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while
the latter silently ignores them.
Examples:
>>> from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, FlaxBeitModel
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> import requests
>>> url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
>>> image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("microsoft/beit-base-patch16-224-pt22k-ft22k")
>>> model = FlaxBeitModel.from_pretrained("microsoft/beit-base-patch16-224-pt22k-ft22k")
>>> inputs = image_processor(images=image, return_tensors="np")
>>> outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> last_hidden_states = outputs.last_hidden_stateFlaxBeitForMaskedImageModeling
class transformers.FlaxBeitForMaskedImageModeling
< source >( config: BeitConfig input_shape = None seed: int = 0 dtype: dtype = <class 'jax.numpy.float32'> _do_init: bool = True **kwargs )
Parameters
- config (BeitConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
- dtype (
jax.numpy.dtype, optional, defaults tojax.numpy.float32) — The data type of the computation. Can be one ofjax.numpy.float32,jax.numpy.float16(on GPUs) andjax.numpy.bfloat16(on TPUs).This can be used to enable mixed-precision training or half-precision inference on GPUs or TPUs. If specified all the computation will be performed with the given
dtype.Note that this only specifies the dtype of the computation and does not influence the dtype of model parameters.
If you wish to change the dtype of the model parameters, see to_fp16() and to_bf16().
Beit Model transformer with a ‘language’ modeling head on top (to predict visual tokens).
This model inherits from FlaxPreTrainedModel. Check the superclass documentation for the generic methods the library implements for all its model (such as downloading, saving and converting weights from PyTorch models)
This model is also a flax.linen.Module subclass. Use it as a regular Flax linen Module and refer to the Flax documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
Finally, this model supports inherent JAX features such as:
__call__
< source >( pixel_values bool_masked_pos = None params: dict = None dropout_rng: PRNGKey = None train: bool = False output_attentions: Optional = None output_hidden_states: Optional = None return_dict: Optional = None ) → transformers.modeling_flax_outputs.FlaxMaskedLMOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Returns
transformers.modeling_flax_outputs.FlaxMaskedLMOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.modeling_flax_outputs.FlaxMaskedLMOutput or a tuple of
torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various
elements depending on the configuration (<class 'transformers.models.beit.configuration_beit.BeitConfig'>) and inputs.
-
logits (
jnp.ndarrayof shape(batch_size, sequence_length, config.vocab_size)) — Prediction scores of the language modeling head (scores for each vocabulary token before SoftMax). -
hidden_states (
tuple(jnp.ndarray), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple ofjnp.ndarray(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the initial embedding outputs.
-
attentions (
tuple(jnp.ndarray), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple ofjnp.ndarray(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length).Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
The FlaxBeitPreTrainedModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module
instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while
the latter silently ignores them.
bool_masked_pos (numpy.ndarray of shape (batch_size, num_patches)):
Boolean masked positions. Indicates which patches are masked (1) and which aren’t (0).
Examples:
>>> from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, BeitForMaskedImageModeling
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> import requests
>>> url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
>>> image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("microsoft/beit-base-patch16-224-pt22k")
>>> model = BeitForMaskedImageModeling.from_pretrained("microsoft/beit-base-patch16-224-pt22k")
>>> inputs = image_processor(images=image, return_tensors="np")
>>> outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> logits = outputs.logitsFlaxBeitForImageClassification
class transformers.FlaxBeitForImageClassification
< source >( config: BeitConfig input_shape = None seed: int = 0 dtype: dtype = <class 'jax.numpy.float32'> _do_init: bool = True **kwargs )
Parameters
- config (BeitConfig) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
- dtype (
jax.numpy.dtype, optional, defaults tojax.numpy.float32) — The data type of the computation. Can be one ofjax.numpy.float32,jax.numpy.float16(on GPUs) andjax.numpy.bfloat16(on TPUs).This can be used to enable mixed-precision training or half-precision inference on GPUs or TPUs. If specified all the computation will be performed with the given
dtype.Note that this only specifies the dtype of the computation and does not influence the dtype of model parameters.
If you wish to change the dtype of the model parameters, see to_fp16() and to_bf16().
Beit Model transformer with an image classification head on top (a linear layer on top of the average of the final hidden states of the patch tokens) e.g. for ImageNet.
This model inherits from FlaxPreTrainedModel. Check the superclass documentation for the generic methods the library implements for all its model (such as downloading, saving and converting weights from PyTorch models)
This model is also a flax.linen.Module subclass. Use it as a regular Flax linen Module and refer to the Flax documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
Finally, this model supports inherent JAX features such as:
__call__
< source >( pixel_values bool_masked_pos = None params: dict = None dropout_rng: PRNGKey = None train: bool = False output_attentions: Optional = None output_hidden_states: Optional = None return_dict: Optional = None ) → transformers.modeling_flax_outputs.FlaxSequenceClassifierOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Returns
transformers.modeling_flax_outputs.FlaxSequenceClassifierOutput or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.modeling_flax_outputs.FlaxSequenceClassifierOutput or a tuple of
torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various
elements depending on the configuration (<class 'transformers.models.beit.configuration_beit.BeitConfig'>) and inputs.
-
logits (
jnp.ndarrayof shape(batch_size, config.num_labels)) — Classification (or regression if config.num_labels==1) scores (before SoftMax). -
hidden_states (
tuple(jnp.ndarray), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple ofjnp.ndarray(one for the output of the embeddings + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the initial embedding outputs.
-
attentions (
tuple(jnp.ndarray), optional, returned whenoutput_attentions=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_attentions=True) — Tuple ofjnp.ndarray(one for each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, sequence_length).Attentions weights after the attention softmax, used to compute the weighted average in the self-attention heads.
The FlaxBeitPreTrainedModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the Module
instance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while
the latter silently ignores them.
Example:
>>> from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, FlaxBeitForImageClassification
>>> from PIL import Image
>>> import requests
>>> url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
>>> image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("microsoft/beit-base-patch16-224")
>>> model = FlaxBeitForImageClassification.from_pretrained("microsoft/beit-base-patch16-224")
>>> inputs = image_processor(images=image, return_tensors="np")
>>> outputs = model(**inputs)
>>> logits = outputs.logits
>>> # model predicts one of the 1000 ImageNet classes
>>> predicted_class_idx = logits.argmax(-1).item()
>>> print("Predicted class:", model.config.id2label[predicted_class_idx])