library_name: transformers
license: mit
metrics:
- bleu
- wer
pipeline_tag: automatic-speech-recognition
tags:
- LLM-as-a-Judge
- chat
- audio
- safetensors
- vllm
datasets:
- MERaLiON/MNSC
base_model:
- openai/whisper-large-v2
widget:
- example_title: Librispeech sample 1
src: /static-proxy?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcdn-media.huggingface.co%2Fspeech_samples%2Fsample1.flac%3C%2Fspan%3E
output:
text: >-
USER: Recognize the speech and give me the transcription.
ASSISTANT:Going along slushy country roads and speaking to damp
audiences in drafty schoolrooms day after day for a fortnight he’ll have
to put in an appearance at some place of worship on sunday morning and
he can come to us immediately afterwards
MERaLiON
MERaLiON-AudioLLM is a Speech-Text Large Language Model tailored for Singapore’s multilingual and multicultural landscape. Integrating a localised Whisper-large-v2 speech encoder and SEA-LION V3 text decoder, MERaLiON-AudioLLM is finetuned on 260,000 hours of speech and audio data, 6 various tasks, to address the diverse linguistic nuances of Singapore's local accents and dialects.
MERaLiON stands for Multimodal Empathetic Reasoning and Learning in One Network.
- Developed by: I2R, A*STAR
- Model type: MultiModal LLM
- Language(s) (Speech): English (Global & Singapore)
- Language(s) (NLP): English, Chinese, Vietnamese, Indonesian, Thai, Filipino, Tamil, Malay, Khmer, Lao, Burmese, Javanese, Sundanese
- License: MIT
We support model inference using the Huggingface and vLLM frameworks. For more technical details, please refer to our report.
Model Description
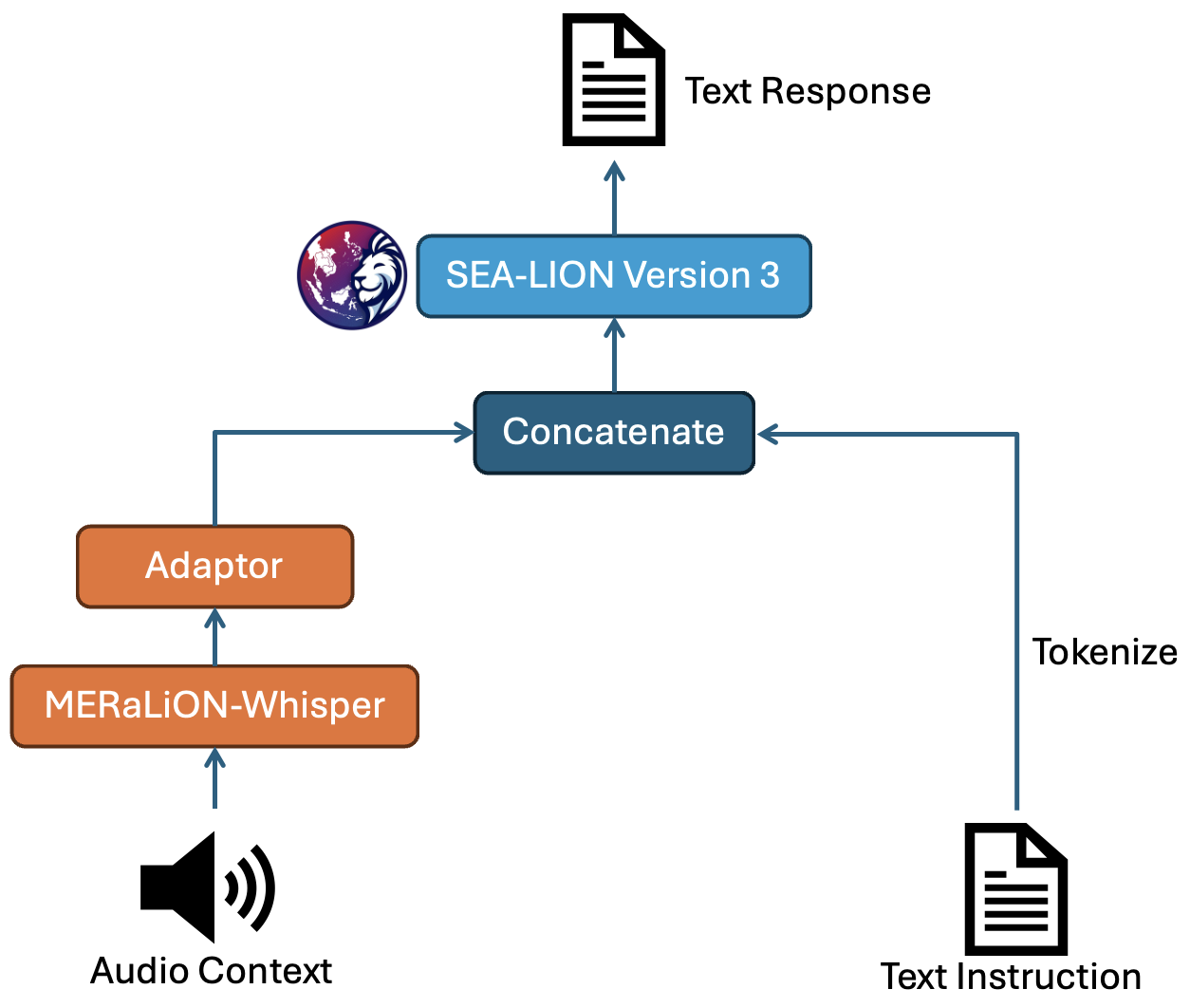
MERaLiON-AudioLLM is designed to take in an audio-text pair as input and generate a text output.
The architecture comprises three key components: an audio encoder that transforms speech or audio inputs into sequences of vector representations, a text decoder that interprets and responds to natural language instructions, and an adaptor module that compresses the encoder representations while aligning the encoder’s hidden dimension with the text decoder’s embedding size.
Specifically, we fine-tuned the MERaLiON-Whisper encoder from Whisper-large-v2 for the audio encoder and used SEA-LION V3, a localised LLM developed by our partner AI Singapore as the text decoder.
Capabilities
MERaLiON-AudioLLM is trained to mainly address 6 tasks, namely Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR),
Speech Translation (ST), Spoken Question Answering (SQA),
Spoken Dialogue Summarization (SDS), Speech Instruction (SI), and Paralinguistics (PARA).
We benchmark MERaLiON-AudioLLM with a series of test sets from the AudioBench benchmark
against three well-known AudioLLMs: Qwen2-Audio 7B, WavLLM, and SALMONN. We also compared with a cascaded model,
which feeds the transcriptions recognized by Whisper-large-v2 and the instruction prompts to a Gemma2 9B CPT SEA-LIONv3 Instruct model to
get the responses. We tuned its hyperparameters and prompt template to optimise performance across
various speech-to-text tasks. As is shown in the following table, MERaLiON-AudioLLM performs better in the Singapore local context,
as evidenced by evaluation results on Singapore's Multitask National Speech Corpus (MNSC) datasets.
MNSC is a multitask speech understanding dataset derived and further annotated from IMDA NSC Corpus. It focuses on the knowledge of Singapore's local accent, localised terms, and code-switching.
We assess ASR and ST tasks using Word Error Rate (WER) and BLEU scores, respectively. For other tasks, we employ the LLM-as-a-Judge framework, which uses a pre-trained large language model to evaluate task performance by generating and scoring responses based on relevance, coherence, and accuracy criteria. Refer to the AudioBench paper for more details.
| Task | Dataset | MERaLiON | Qwen2-Audio 7B | WavLLM | SALMONN-7B | Cascaded Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Automatic Speech Recognition WER (↓) |
LibriSpeech-Test-Clean | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.10 | 0.03 |
| LibriSpeech-Test-Other | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.05 | |
| Common-Voice-15-En-Test | 0.10 | 0.11 | 0.15 | 0.31 | 0.11 | |
| Earnings21-Test | 0.17 | 0.19 | 0.65 | 0.26 | 0.11 | |
| Earnings22-Test | 0.20 | 0.24 | 0.67 | 0.36 | 0.14 | |
| MNSC-ASR-Part 1 | 0.05 | 0.07 | - | 0.09 | 0.07 | |
| MNSC-ASR-Part 2 | 0.05 | 0.19 | - | 0.42 | 0.33 | |
| MNSC-ASR-Part 3 | 0.28 | 0.35 | - | 0.66 | 0.30 | |
| MNSC-ASR-Part 4 | 0.40 | 0.56 | - | 0.76 | 0.48 | |
| MNSC-ASR-Part 5 | 0.21 | 0.28 | - | 0.35 | 0.23 | |
| MNSC-ASR-Part 6 | 0.15 | 0.22 | - | 0.25 | 0.18 | |
| Speech Translation BLEU (↑) |
CoVoST 2 En → Id | 32.62 | 16.33 | 13.84 | 14.14 | 27.62 |
| CoVoST 2 En → Zh | 37.98 | 25.77 | 31.96 | 33.89 | 35.27 | |
| CoVoST 2 En → Ta | 8.50 | 0.03 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 8.46 | |
| CoVoST 2 Id → En | 37.07 | 6.33 | 5.93 | 26.89 | 46.80 | |
| CoVoST 2 Zh → En | 15.01 | 16.47 | 2.37 | 5.30 | 15.21 | |
| CoVoST 2 Ta → En | 3.97 | 0.04 | 0.17 | 0.36 | 2.83 | |
| Spoken Question Answering LLM-as-a-Judge (↑) |
SLUE-SQA-5 | 82.94 | 80.05 | 83.92 | 83.48 | 88.58 |
| Spoken-SQuAD | 70.33 | 64.86 | 77.65 | 66.40 | 88.62 | |
| CN-College-Listen-Test | 85.03 | 74.51 | 65.43 | 50.90 | 91.85 | |
| Singapore-Public-Speech-SQA | 60.32 | 58.31 | 58.55 | 59.24 | 73.11 | |
| MNSC-SQA-Part 3 | 51.4 | 42.0 | - | 40.60 | 53.20 | |
| MNSC-SQA-Part 4 | 49.0 | 39.6 | - | 36.60 | 60.20 | |
| MNSC-SQA-Part 5 | 58.2 | 51.6 | - | 44.60 | 67.20 | |
| MNSC-SQA-Part 6 | 65.2 | 53.6 | - | 46.80 | 71.60 | |
| Spoken Dialogue Summarization LLM-as-a-Judge (↑) |
MNSC-SDS-Part 3 | 46.80 | 33.80 | - | 9.0 | 45.40 |
| MNSC-SDS-Part 4 | 45.80 | 24.80 | - | 7.0 | 44.00 | |
| MNSC-SDS-Part 5 | 55.2 | 40.4 | - | 17.2 | 58.00 | |
| MNSC-SDS-Part 6 | 61.8 | 46.2 | - | 24.2 | 65.40 | |
| Speech Instruction LLM-as-a-Judge (↑) |
OpenHermes-Audio | 71.4 | 44.8 | 22.40 | 15.80 | 72.20 |
| Alpaca-GPT4-Audio | 73.4 | 52.6 | 21.60 | 17.20 | 73.80 | |
| Paralinguistics LLM-as-a-Judge (↑) |
VoxCeleb-Gender-Test | 99.53 | 99.12 | 69.68 | 88.81 | 35.25 |
| VoxCeleb-Accent-Test | 46.35 | 29.18 | - | 34.22 | 24.64 | |
| MELD-Sentiment-Test | 42.26 | 53.49 | 50.08 | 42.07 | 56.67 | |
| MELD-Emotion-Test | 30.15 | 40.54 | 41.07 | 30.73 | 47.39 |
Uses
Here we provide a code snippet illustrating the process of loading both the processor and model, alongside detailed instructions on executing the MERaLiON-AudioLLM model for content generation.
Out of Scope use: This model is not intended for use in tool calling, math, and coding tasks.
Inference
from datasets import load_dataset
from transformers import AutoModelForSpeechSeq2Seq, AutoProcessor
repo_id = "MERaLiON/MERaLiON-AudioLLM-Whisper-SEA-LION"
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(
repo_id,
trust_remote_code=True,
)
model = AutoModelForSpeechSeq2Seq.from_pretrained(
repo_id,
use_safetensors=True,
trust_remote_code=True,
)
prompt = "Given the following audio context: <SpeechHere>\n\nText instruction: {query}"
query = "Please transcribe this speech."
conversation = [
{"role": "user", "content": prompt.format(query=query)}
]
chat_prompt = processor.tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
conversation=conversation,
tokenize=False,
add_generation_prompt=True
)
libri_data = load_dataset("distil-whisper/librispeech_long", "clean", split="validation")
audio_array = libri_data[0]["audio"]["array"]
inputs = processor(text=chat_prompt, audios=audio_array)
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=128)
generated_ids = outputs[:, inputs['input_ids'].size(1):]
response = processor.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)[0]
Batch Inference
MERaLiON-AudioLLM also supports batch inference.
from datasets import load_dataset
from transformers import AutoModelForSpeechSeq2Seq, AutoProcessor
repo_id = "MERaLiON/MERaLiON-AudioLLM-Whisper-SEA-LION"
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(
repo_id,
trust_remote_code=True,
)
model = AutoModelForSpeechSeq2Seq.from_pretrained(
repo_id,
use_safetensors=True,
trust_remote_code=True,
)
prompt = "Given the following audio context: <SpeechHere>\n\nText instruction: {query}"
transcribe_query = "Please transcribe this speech."
translate_query = "Can you please translate this speech into written Chinese?"
conversation = [
[{"role": "user", "content": prompt.format(query=transcribe_query)}],
[{"role": "user", "content": prompt.format(query=translate_query)}],
]
chat_prompt = processor.tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
conversation=conversation,
tokenize=False,
add_generation_prompt=True
)
libri_data = load_dataset("distil-whisper/librispeech_long", "clean", split="validation")
audio_array = [libri_data[0]["audio"]["array"]]*2
inputs = processor(text=chat_prompt, audios=audio_array)
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=128)
generated_ids = outputs[:, inputs['input_ids'].size(1):]
response = processor.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
vLLM Inference
MERaLiON-AudioLLM requires vLLM version 0.6.4.post1.
pip install vllm==0.6.4.post1
Here is an example of offline inference using our custom vLLM class.
import torch
from vllm import ModelRegistry, LLM, SamplingParams
from vllm.assets.audio import AudioAsset
# register custom MERaLiON-AudioLLM class
from .vllm_meralion import MERaLiONForConditionalGeneration
ModelRegistry.register_model("MERaLiONForConditionalGeneration", MERaLiONForConditionalGeneration)
def run_meralion(question: str):
model_name = "MERaLiON/MERaLiON-AudioLLM-Whisper-SEA-LION"
llm = LLM(model=model_name,
tokenizer=model_name,
tokenizer_mode="slow",
max_model_len=4096,
max_num_seqs=5,
limit_mm_per_prompt={"audio": 1},
trust_remote_code=True,
dtype=torch.bfloat16
)
audio_in_prompt = "Given the following audio context: <SpeechHere>\n\n"
prompt = ("<start_of_turn>user\n"
f"{audio_in_prompt}Text instruction: {question}<end_of_turn>\n"
"<start_of_turn>model\n")
stop_token_ids = None
return llm, prompt, stop_token_ids
audio_asset = AudioAsset("mary_had_lamb")
question= "Please trancribe this speech."
llm, prompt, stop_token_ids = run_meralion(question)
# We set temperature to 0.2 so that outputs can be different
# even when all prompts are identical when running batch inference.
sampling_params = SamplingParams(temperature=0.2,
max_tokens=64,
stop_token_ids=stop_token_ids)
mm_data = {"audio": [audio_asset.audio_and_sample_rate]}
inputs = {"prompt": prompt, "multi_modal_data": mm_data}
# batch inference
inputs = [inputs] * 2
outputs = llm.generate(inputs, sampling_params=sampling_params)
for o in outputs:
generated_text = o.outputs[0].text
print(generated_text)
Disclaimer
The current MERaLiON-AudioLLM has not been specifically aligned for safety and may generate content that is inappropriate, offensive, or harmful. Developers and users are responsible for performing their own safety fine-tuning and implementing necessary security measures. The authors shall not be held liable for any claims, damages, or other liabilities arising from the use of the released models, weights, or code.
This research is supported by the National Research Foundation, Singapore, and Infocomm Media Development Authority, Singapore under its National Large Language Models Funding Initiative. Any opinions, findings and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the author(s) and do not reflect the views of National Research Foundation, Singapore and Infocomm Media Development Authority, Singapore.
Technical Specifications
Training Data
MERaLiON-AudioLLM is trained on a diverse collection of publicly available datasets, alongside synthesised and augmented samples carefully curated by the team and native speakers, totaling 260,000 hours of audio.
Compute and Infrastructure
MERaLiON-AudioLLM is trained on the ASPIRE 2A+ Supercomputer Cluster, provided by National Supercomputing Centre (NSCC), Singapore. ASPIRE 2A+ cluster provides multiple H100 nodes, with each compute node equipped with 8 Nvidia H100 GPUs, 2 TB of RAM, and 30 TB of locally attached NVMe storage. These nodes are interconnected via a rail-optimised, full fat-tree topology, utilising 400 Gb/s NDR InfiniBand cables. Additionally, the cluster incorporates a 2.5 PB SSD-based Lustre file system, linked to the H100 nodes through high-speed InfiniBand connections.
With a global batch size of 640, we train the current release of MERaLiON-AudioLLM for around 200k steps, which took 2 days to complete using 16 nodes, 128 H100 GPUs.
Citation
BibTeX:
[More Information Needed]
APA:
[More Information Needed]