# MinerU
## Introduction
MinerU is a one-stop, open-source, high-quality data extraction tool, includes the following primary features:
- [Magic-PDF](#Magic-PDF) PDF Document Extraction
- [Magic-Doc](#Magic-Doc) Webpage & E-book Extraction
# Magic-PDF
## Introduction
Magic-PDF is a tool designed to convert PDF documents into Markdown format, capable of processing files stored locally or on object storage supporting S3 protocol.
Key features include:
- Support for multiple front-end model inputs
- Removal of headers, footers, footnotes, and page numbers
- Human-readable layout formatting
- Retains the original document's structure and formatting, including headings, paragraphs, lists, and more
- Extraction and display of images and tables within markdown
- Conversion of equations into LaTeX format
- Automatic detection and conversion of garbled PDFs
- Compatibility with CPU and GPU environments
- Available for Windows, Linux, and macOS platforms
https://github.com/opendatalab/MinerU/assets/11393164/618937cb-dc6a-4646-b433-e3131a5f4070
## Project Panorama
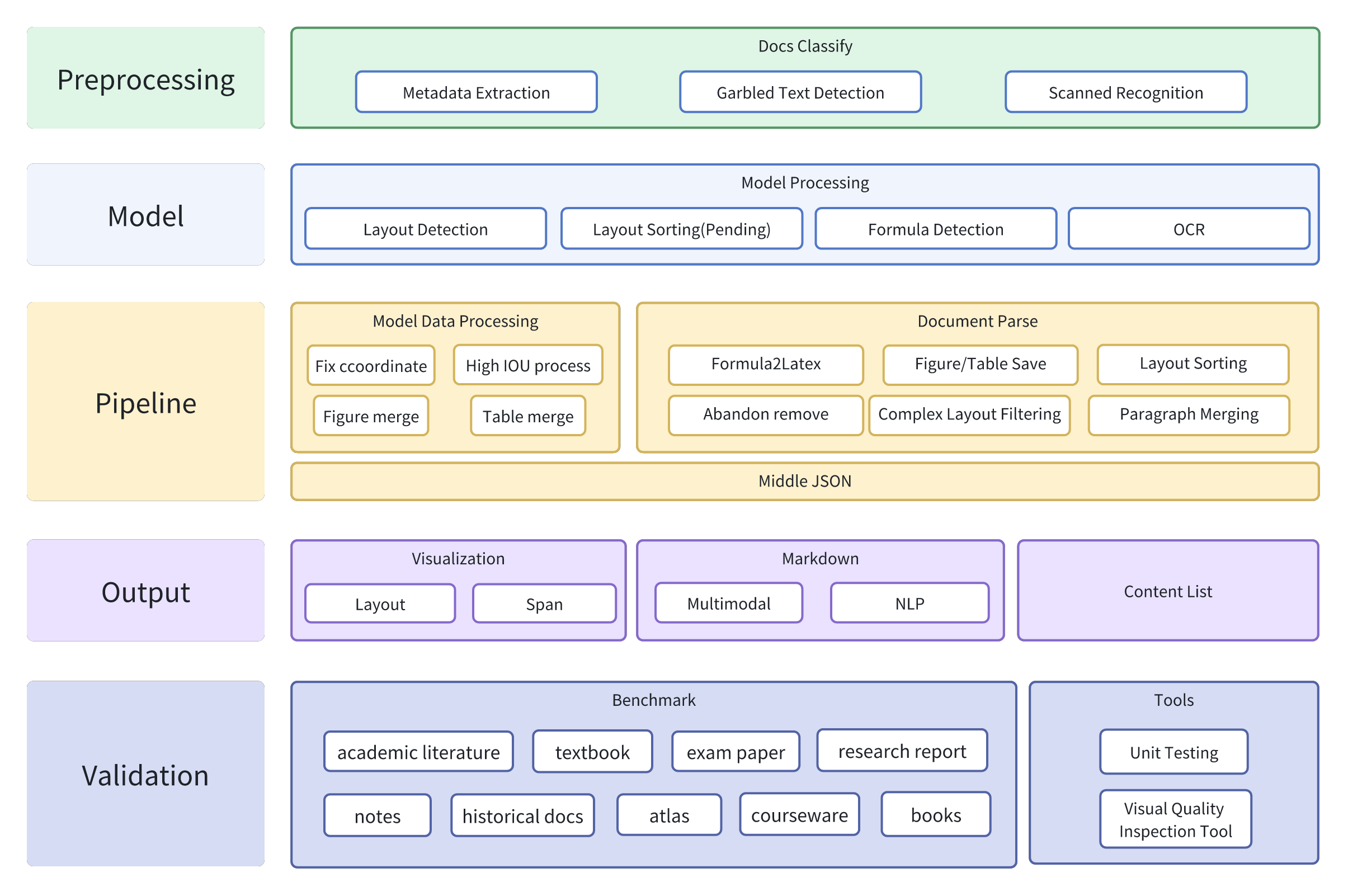
## Flowchart

### Dependency repositorys
- [PDF-Extract-Kit : A Comprehensive Toolkit for High-Quality PDF Content Extraction](https://github.com/opendatalab/PDF-Extract-Kit) 🚀🚀🚀
## Getting Started
### Requirements
- Python >= 3.9
Using a virtual environment is recommended to avoid potential dependency conflicts; both venv and conda are suitable.
For example:
```bash
conda create -n MinerU python=3.10
conda activate MinerU
```
### Installation and Configuration
#### 1. Install Magic-PDF
Install the full-feature package with pip:
>Note: The pip-installed package supports CPU-only and is ideal for quick tests.
>
>For CUDA/MPS acceleration in production, see [Acceleration Using CUDA or MPS](#4-Acceleration-Using-CUDA-or-MPS).
```bash
pip install magic-pdf[full-cpu]
```
The full-feature package depends on detectron2, which requires a compilation installation.
If you need to compile it yourself, please refer to https://github.com/facebookresearch/detectron2/issues/5114
Alternatively, you can directly use our precompiled whl package (limited to Python 3.10):
```bash
pip install detectron2 --extra-index-url https://myhloli.github.io/wheels/
```
#### 2. Downloading model weights files
For detailed references, please see below [how_to_download_models](docs/how_to_download_models_en.md)
After downloading the model weights, move the 'models' directory to a directory on a larger disk space, preferably an SSD.
#### 3. Copy the Configuration File and Make Configurations
You can get the [magic-pdf.template.json](magic-pdf.template.json) file in the repository root directory.
```bash
cp magic-pdf.template.json ~/magic-pdf.json
```
In magic-pdf.json, configure "models-dir" to point to the directory where the model weights files are located.
```json
{
"models-dir": "/tmp/models"
}
```
#### 4. Acceleration Using CUDA or MPS
If you have an available Nvidia GPU or are using a Mac with Apple Silicon, you can leverage acceleration with CUDA or MPS respectively.
##### CUDA
You need to install the corresponding PyTorch version according to your CUDA version.
This example installs the CUDA 11.8 version.More information https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/
```bash
pip install --force-reinstall torch==2.3.1 torchvision==0.18.1 --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu118
```
Also, you need to modify the value of "device-mode" in the configuration file magic-pdf.json.
```json
{
"device-mode":"cuda"
}
```
##### MPS
For macOS users with M-series chip devices, you can use MPS for inference acceleration.
You also need to modify the value of "device-mode" in the configuration file magic-pdf.json.
```json
{
"device-mode":"mps"
}
```
### Usage
#### 1.Usage via Command Line
###### simple
```bash
magic-pdf pdf-command --pdf "pdf_path" --inside_model true
```
After the program has finished, you can find the generated markdown files under the directory "/tmp/magic-pdf".
You can find the corresponding xxx_model.json file in the markdown directory.
If you intend to do secondary development on the post-processing pipeline, you can use the command:
```bash
magic-pdf pdf-command --pdf "pdf_path" --model "model_json_path"
```
In this way, you won't need to re-run the model data, making debugging more convenient.
###### more
```bash
magic-pdf --help
```
#### 2. Usage via Api
###### Local
```python
image_writer = DiskReaderWriter(local_image_dir)
image_dir = str(os.path.basename(local_image_dir))
jso_useful_key = {"_pdf_type": "", "model_list": []}
pipe = UNIPipe(pdf_bytes, jso_useful_key, image_writer)
pipe.pipe_classify()
pipe.pipe_parse()
md_content = pipe.pipe_mk_markdown(image_dir, drop_mode="none")
```
###### Object Storage
```python
s3pdf_cli = S3ReaderWriter(pdf_ak, pdf_sk, pdf_endpoint)
image_dir = "s3://img_bucket/"
s3image_cli = S3ReaderWriter(img_ak, img_sk, img_endpoint, parent_path=image_dir)
pdf_bytes = s3pdf_cli.read(s3_pdf_path, mode=s3pdf_cli.MODE_BIN)
jso_useful_key = {"_pdf_type": "", "model_list": []}
pipe = UNIPipe(pdf_bytes, jso_useful_key, s3image_cli)
pipe.pipe_classify()
pipe.pipe_parse()
md_content = pipe.pipe_mk_markdown(image_dir, drop_mode="none")
```
Demo can be referred to [demo.py](demo/demo.py)
# Magic-Doc
## Introduction
Magic-Doc is a tool designed to convert web pages or multi-format e-books into markdown format.
Key Features Include:
- Web Page Extraction
- Cross-modal precise parsing of text, images, tables, and formula information.
- E-Book Document Extraction
- Supports various document formats including epub, mobi, with full adaptation for text and images.
- Language Type Identification
- Accurate recognition of 176 languages.
https://github.com/opendatalab/MinerU/assets/11393164/a5a650e9-f4c0-463e-acc3-960967f1a1ca
https://github.com/opendatalab/MinerU/assets/11393164/0f4a6fe9-6cca-4113-9fdc-a537749d764d
https://github.com/opendatalab/MinerU/assets/11393164/20438a02-ce6c-4af8-9dde-d722a4e825b2
## Project Repository
- [Magic-Doc](https://github.com/InternLM/magic-doc)
Outstanding Webpage and E-book Extraction Tool
# All Thanks To Our Contributors
# License Information
[LICENSE.md](LICENSE.md)
The project currently leverages PyMuPDF to deliver advanced functionalities; however, its adherence to the AGPL license may impose limitations on certain use cases. In upcoming iterations, we intend to explore and transition to a more permissively licensed PDF processing library to enhance user-friendliness and flexibility.
# Acknowledgments
- [PaddleOCR](https://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleOCR)
- [PyMuPDF](https://github.com/pymupdf/PyMuPDF)
- [fast-langdetect](https://github.com/LlmKira/fast-langdetect)
- [pdfminer.six](https://github.com/pdfminer/pdfminer.six)
# Citation
```bibtex
@misc{2024mineru,
title={MinerU: A One-stop, Open-source, High-quality Data Extraction Tool},
author={MinerU Contributors},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/opendatalab/MinerU}},
year={2024}
}
```
# Star History